Echogenic liver refers to a condition where the liver appears brighter than usual on an ultrasound due to increased sound wave reflections (echogenicity). This is often an indication of fatty liver disease or other liver conditions.
Echogenic Liver Health
Causes of Echogenic Liver
An echogenic liver is typically a result of fat accumulation in liver cells, which can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Fat buildup in the liver not caused by alcohol consumption.
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Caused by excessive alcohol intake.
- Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver that can increase liver echogenicity.
- Cirrhosis: Long-term damage to the liver leading to scarring and increased echogenicity.
- Obesity or Diabetes: These conditions are often linked to fatty liver and increased liver echogenicity.
- Metabolic Syndrome: A combination of conditions like high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels can lead to fatty liver.
Symptoms Associated with Echogenic Liver
Many people with an echogenic liver may not experience noticeable symptoms, but some signs could include:
- Fatigue
- Discomfort or pain in the upper right abdomen
- Enlarged liver (hepatomegaly)
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) in more advanced liver disease
Diagnosis
The most common way to diagnose an echogenic liver is through ultrasound imaging. If the liver appears echogenic, additional tests may be recommended to determine the underlying cause, such as:
- Blood Tests: To check liver enzyme levels and rule out liver inflammation or damage.
- CT or MRI Scans: More detailed imaging tests may be needed for a clearer diagnosis.
- Liver Biopsy: In rare cases, a biopsy may be performed to assess the extent of liver damage.
Treatment and Management
Managing echogenic liver primarily involves addressing the underlying cause. Here are general strategies:
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Diet: A low-fat, balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce liver fat.
- Weight Loss: For individuals with NAFLD or obesity, gradual weight loss can improve liver health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can lower fat levels in the liver and improve overall metabolic health.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Reducing or eliminating alcohol is crucial if alcohol is contributing to liver damage.
- Medical Treatment:
- Medications: There are currently no specific medications for fatty liver, but doctors may prescribe medications to manage risk factors like high cholesterol, diabetes, or high blood pressure.
- Managing Diabetes: If you have diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is critical for liver health.
- Monitoring: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are important to monitor liver function and prevent further complications.
Prevention
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a liver-friendly diet, avoiding high-fat, high-sugar foods, and incorporating more lean proteins and fiber-rich foods can reduce the risk of fatty liver.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise, even moderate, helps reduce liver fat and improve overall health.
- Avoid Excessive Alcohol: Limiting alcohol intake significantly reduces the risk of liver disease.
When to See a Doctor
If you have risk factors like obesity, diabetes, or a history of heavy alcohol use, and you experience symptoms such as fatigue or upper abdominal discomfort, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and possible liver imaging.
Conclusion
An echogenic liver is often a sign of fatty liver disease, which can be managed through lifestyle changes and regular monitoring. Early detection and proactive management can prevent more serious liver complications like cirrhosis or liver failure. Always follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for the best outcomes.
icd 10 code for fatty liver
The ICD-10 code for fatty liver disease (also known as hepatic steatosis) is K76.0.
ICD-10 Code for Fatty Liver: K76.0
- Description: Fatty (change of) liver, not elsewhere classified.
- Applicable for: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), hepatic steatosis, and conditions where there is fat accumulation in liver cells, unrelated to alcohol use.
- Excludes: Alcoholic liver disease (which falls under different codes like K70.0 for alcoholic fatty liver).
Details of K76.0 – Fatty Liver
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
NAFLD is one of the most common causes of fatty liver and is generally classified under K76.0 when not related to alcohol consumption. NAFLD can range from simple fat accumulation (steatosis) to Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), which can lead to inflammation and liver damage.
- K76.0 is used when the cause of fatty liver is metabolic or other factors not involving alcohol.
- NAFLD is often associated with obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome.
Exclusion Notes:
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease is classified differently under K70.0 for alcoholic-related liver disease. This classification is reserved for liver conditions directly caused by alcohol consumption.
Related Conditions and Codes:
- NASH (Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis): Also classified under K76.0, but if the condition progresses to cirrhosis or another advanced liver disease, different ICD codes may apply, depending on severity.
- Alcoholic Liver Disease:
- K70.0: Alcoholic fatty liver.
- K70.1: Alcoholic hepatitis.
- K70.2: Alcoholic fibrosis and sclerosis of the liver.
- K70.3: Alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver.
- Other Liver Disease Codes:
- K75.9: Inflammatory liver disease, unspecified (may be used if the specific type of liver inflammation isn’t clear).
ICD-10 for Associated Conditions:
- E66.0: Obesity, which is a major risk factor for developing NAFLD.
- E11.9: Type 2 diabetes mellitus, often linked to the development of fatty liver.
- E78.5: Hyperlipidemia, another associated risk factor for fatty liver.
When to Use K76.0:
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: When there is fat buildup in the liver cells due to causes unrelated to alcohol consumption.
- Simple Steatosis: If the condition is detected early and there’s no significant inflammation or liver damage.
- Steatohepatitis (NASH): When the condition progresses from simple fat buildup to liver inflammation and injury but still falls under non-alcoholic causes.
Conclusion
The ICD-10 code K76.0 is used to classify fatty liver when not caused by alcohol, covering both simple hepatic steatosis and NAFLD. For alcoholic fatty liver or more advanced conditions like cirrhosis, other specific codes are applied. It’s important to differentiate the cause of the fatty liver to use the correct ICD-10 code in medical documentation.
7 day meal plan for fatty liver
A 7-day meal plan for fatty liver disease focuses on reducing fat accumulation in the liver, improving liver function, and promoting overall health. The diet should be rich in whole foods, fiber, lean proteins, healthy fats, and antioxidants while limiting processed foods, added sugars, unhealthy fats, and excessive carbohydrates. Here’s a sample plan:
General Guidelines:
- Include: Vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean protein (chicken, fish, legumes), healthy fats (avocado, olive oil), and high-fiber foods.
- Avoid: Sugary foods, refined carbohydrates, saturated fats, alcohol, and processed foods.
7-Day Meal Plan for Fatty Liver
Day 1:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with chia seeds, berries, and a drizzle of honey
- Snack: A small apple with a handful of almonds
- Lunch: Grilled chicken breast salad with mixed greens, cucumbers, tomatoes, and olive oil dressing
- Snack: Carrot sticks with hummus
- Dinner: Baked salmon with steamed broccoli and quinoa
- Drink: Green tea or water with lemon
Day 2:
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt with flaxseeds, walnuts, and blueberries
- Snack: Sliced cucumber with a sprinkle of sea salt
- Lunch: Lentil soup with a side of whole-grain bread
- Snack: Sliced bell peppers and hummus
- Dinner: Stir-fried tofu with mixed vegetables (broccoli, bell peppers, spinach) and brown rice
- Drink: Herbal tea or infused water (cucumber or mint)
Day 3:
- Breakfast: Smoothie with spinach, banana, almond milk, chia seeds, and a scoop of protein powder
- Snack: A handful of mixed nuts (almonds, walnuts)
- Lunch: Grilled turkey breast wrap with whole wheat tortilla, avocado, lettuce, and tomato
- Snack: Baby carrots with guacamole
- Dinner: Baked chicken thighs with roasted sweet potatoes and steamed asparagus
- Drink: Water with lemon
Day 4:
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with spinach, tomatoes, and avocado slices
- Snack: A small pear with a tablespoon of almond butter
- Lunch: Quinoa salad with chickpeas, cucumbers, tomatoes, and lemon vinaigrette
- Snack: A handful of unsalted pumpkin seeds
- Dinner: Grilled shrimp with a side of sautéed kale and brown rice
- Drink: Herbal tea or water
Day 5:
- Breakfast: Whole wheat toast with avocado and a poached egg
- Snack: Fresh berries (blueberries, strawberries)
- Lunch: Grilled salmon over mixed greens with a light olive oil and balsamic vinegar dressing
- Snack: Sliced cucumber with hummus
- Dinner: Baked cod with roasted Brussels sprouts and a side of quinoa
- Drink: Green tea or lemon water
Day 6:
- Breakfast: Smoothie with kale, pineapple, banana, chia seeds, and almond milk
- Snack: A handful of walnuts or sunflower seeds
- Lunch: Chicken and vegetable stir-fry with broccoli, carrots, and brown rice
- Snack: A small orange with a handful of almonds
- Dinner: Turkey meatballs with a side of zucchini noodles and marinara sauce
- Drink: Water with cucumber or mint
Day 7:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with flaxseeds, cinnamon, and sliced banana
- Snack: Sliced apple with a tablespoon of peanut butter
- Lunch: Black bean and avocado salad with cherry tomatoes, red onions, and lime vinaigrette
- Snack: Celery sticks with almond butter
- Dinner: Grilled chicken breast with roasted cauliflower and sweet potato
- Drink: Herbal tea or lemon water
Additional Tips:
- Hydrate: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Adding lemon or cucumber slices can aid in digestion.
- Exercise: Incorporate regular physical activity, as exercise helps improve liver health.
- Portion Control: Keep portion sizes in check to avoid overeating and support weight management.
- Avoid Processed Foods and Sugar: Reduce consumption of processed snacks, sugary drinks, and refined carbs.
Foods to Prioritize:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, broccoli
- High-Fiber Foods: Oats, quinoa, brown rice, lentils
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil, avocado, nuts, seeds
- Lean Protein: Chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, legumes
- Antioxidant-Rich Fruits: Berries, oranges, apples
Foods to Avoid:
- Sugary Foods: Soda, candies, baked goods
- Refined Carbohydrates: White bread, pasta, pastries
- Saturated and Trans Fats: Fried foods, fast food, fatty cuts of meat
- Alcohol: Eliminating or minimizing alcohol intake is critical for liver health.
This 7-day meal plan aims to reduce fat in the liver, improve liver function, and support overall well-being. Always consult a healthcare professional or a dietitian for personalized advice, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
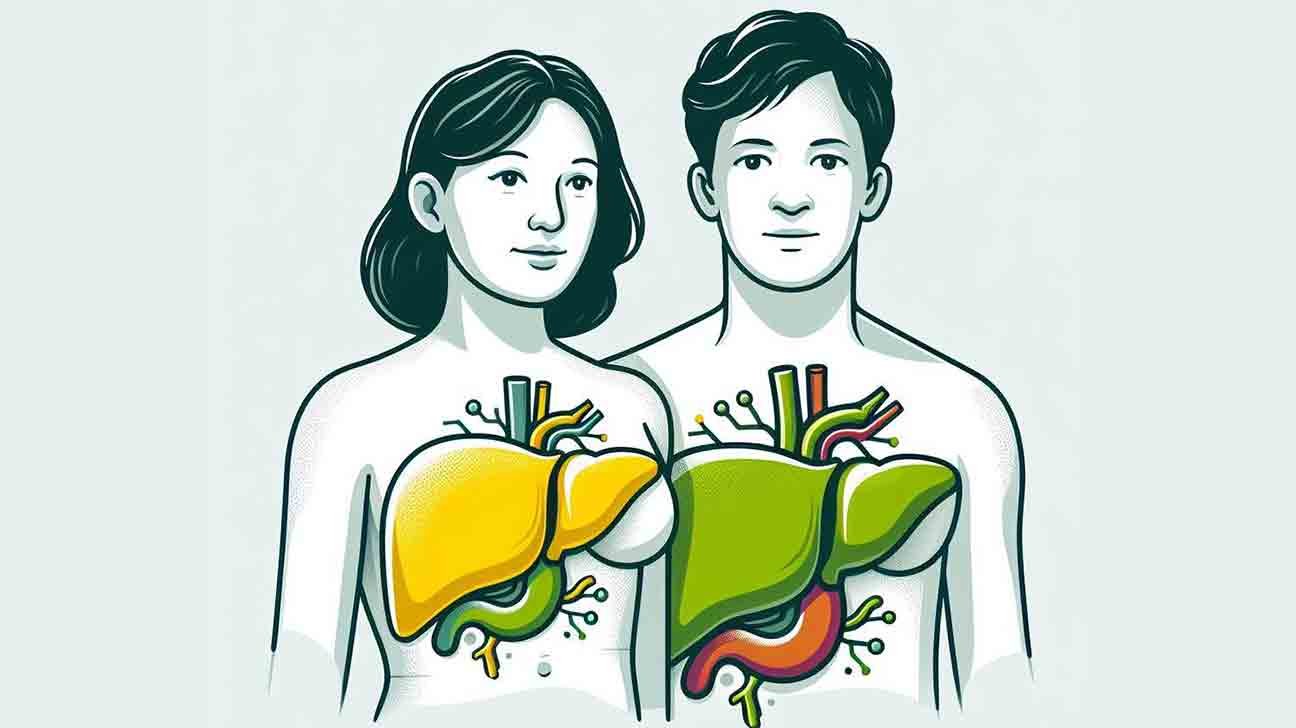
The liver is a vital organ in the human body responsible for filtering blood and detoxifying harmful substances. It also produces bile to aid in digestion.
The liver is located on the right side of the abdomen and weighs about three pounds in adults. The liver is one of the largest organs in the body and performs many essential functions. It is responsible for processing nutrients, producing bile, and eliminating toxins from the body.
The liver also plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels, producing cholesterol, and storing vitamins and minerals. Due to its critical functions, any damage or disease to the liver can have severe consequences on a person’s health. Liver disease can be caused by various factors, including alcohol abuse, hepatitis B and C, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. It’s essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle to keep the liver functioning correctly, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
Fatty Liver
Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells. It can result from various causes, including alcohol consumption, obesity, and certain medical conditions. Fatty liver can lead to liver inflammation and damage if not managed properly, potentially progressing to more severe liver diseases.
Understanding Fatty Liver
Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver cells. This condition can be categorized into two types: alcoholic disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Causes Of Fatty Liver:
- Obesity: Obesity is a significant risk factor for the development of fatty liver. Excessive body weight can lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver.
- Poor Diet: Consuming a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can contribute to the development of fatty liver.
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance, commonly associated with type 2 diabetes, can lead to an increased accumulation of fat in the liver.
Symptoms Of Fatty Liver:
- Fatigue: Individuals with fatty liver may experience persistent fatigue due to the compromised liver function.
- Abdominal Discomfort: Some people with fatty liver may experience discomfort or pain in the upper right abdomen.
- Enlarged Liver: In some cases, the liver may become enlarged, leading to a feeling of fullness or discomfort in the abdomen.

Treatment And Prevention Of Fatty Liver:
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity can help reduce the accumulation of fat in the liver.
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while minimizing the consumption of processed foods and sugary beverages can support liver health.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can aid in weight management and improve overall liver function.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and methods of managing fatty liver, individuals can take proactive steps to support liver health and prevent the progression of this condition.
Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is a condition that affects the liver, causing fat buildup and potential liver damage. It can be caused by obesity, alcohol consumption, or certain medications. Treatment usually involves lifestyle changes such as weight loss and avoiding alcohol.
Fatty Liver Disease: Understanding The Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment Options
The liver is an essential organ in the body responsible for a variety of vital functions. However, certain conditions can affect the liver’s ability to function correctly, leading to serious health problems. One such condition is , a condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
Fatty liver disease is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent further complications. We will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for fatty liver disease.
What Is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease is a condition characterized by the buildup of fat in the liver cells. This accumulation of fat in the liver can lead to liver inflammation, scarring, and even liver failure. There are two main types of fatty liver disease: alcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Causes Of Fatty Liver Disease
Alcoholic fatty liver disease is caused by excessive alcohol consumption, leading to the accumulation of fat in the liver cells. On the other hand, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Obesity
- Insulin resistance
- High blood sugar
- High levels of triglycerides in the blood
- Rapid weight loss
- Malnutrition
- Certain medications

Symptoms Of Fatty Liver Disease
In most cases, fatty liver disease does not cause any symptoms in its early stages. However, as the condition progresses, some people may experience the following symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Swelling in the legs and abdomen
Treatment Options For Fatty Liver Disease
The treatment for fatty liver disease depends on the underlying cause of the condition. For alcoholic fatty liver disease, the primary treatment is to stop drinking alcohol. For nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, treatment options include:
- Lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, regular exercise, and a healthy diet
- Medications to control cholesterol and blood sugar levels
- Vitamin E supplements
- Liver transplant (in severe cases)
Fatty liver disease is a serious condition that can lead to severe health complications if left untreated. If you experience any symptoms of fatty liver disease, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. With proper diagnosis and treatment, the outlook for people with fatty liver disease is generally positive.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, and abdominal discomfort. As the condition progresses, it can lead to liver damage and other complications. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms.
Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the buildup of fat in the liver cells. This can lead to inflammation and damage to the liver if left untreated. Recognizing the symptoms of fatty liver is crucial for early detection and appropriate management.
Here are some common signs and indicators to watch out for:
- Abdominal discomfort: Many individuals with fatty liver experience discomfort or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. This can range from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation.
- Fatigue: Feeling constantly tired and lacking energy is a common symptom of fatty liver. The liver’s impaired function can result in decreased energy levels.
- Weight gain: Unexplained weight gain, especially around the abdomen, may be an indication of fatty liver. The liver’s compromised ability to metabolize fat can contribute to weight gain.
- Jaundice: In severe cases, fatty liver can lead to jaundice, a condition characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes. This occurs when the liver is unable to process bilirubin effectively.
- Poor appetite: Individuals with fatty liver often experience a decreased appetite and may have difficulty tolerating fatty or greasy foods.
- Nausea and vomiting: Fatty liver can cause persistent nausea and occasional vomiting, particularly after consuming fatty meals.
- Swollen abdomen: As the liver becomes inflamed and enlarged, it can lead to the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, resulting in bloating and a distended appearance.
- Elevated liver enzymes: Blood tests may reveal elevated levels of liver enzymes, such as alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), indicating liver inflammation and damage.
If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect you may have fatty liver, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate management. Early detection and lifestyle modifications can help prevent further liver damage and improve overall liver health.

Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Cirrhosis of the liver is a chronic and progressive condition that damages the liver, causing scar tissue to replace healthy tissue. This can lead to liver failure and a host of other complications, including fluid buildup, bleeding, and confusion.
The liver is a vital organ in the body responsible for various functions, including detoxification and metabolism. However, certain factors can lead to liver damage, with cirrhosis being one of the most severe conditions. In this section, we will discuss , its causes, symptoms, and possible treatments.
Causes Of Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Cirrhosis of the liver is caused by various factors, including:
- Chronic alcohol abuse
- Hepatitis B or C
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Inherited disorders such as Wilson’s disease and hemochromatosis
Symptoms Of Cirrhosis Of The Liver
The symptoms of cirrhosis of the liver may not be noticeable in the early stages. However, as the condition progresses, the following symptoms may occur:
- Fatigue
- Itchy skin
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Swelling in the legs, feet, or ankles
- Abdominal swelling or pain
- Loss of appetite or weight loss
- Nausea and vomiting
Treatment Options For Cirrhosis Of The Liver
The treatment for cirrhosis of the liver depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Here are some possible treatment options:
- Lifestyle changes such as avoiding alcohol and maintaining a healthy diet
- Medications to manage symptoms and complications
- Liver transplant for severe cases
It’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent further liver damage and improve your quality of life.
Remember, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial in preventing liver damage. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting vaccinated for hepatitis B are some of the ways to protect your liver.
Liver Disease
Liver disease is a condition that affects the liver, causing inflammation and damage. It can be caused by various factors such as alcohol abuse, viral infections, or obesity. Early detection and proper treatment are crucial for managing liver disease and preventing complications.
The liver is one of the most important organs in the body. It performs various critical functions such as detoxification, protein synthesis, and bile production. However, the liver is susceptible to various diseases that can impact its ability to function correctly.
In this blog post, we’ll focus on and explore its causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Causes Of Liver Disease
Liver disease can be caused by various factors, including:
- Alcohol abuse
- Viral hepatitis
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Autoimmune disorders
- Genetics
Symptoms Of Liver Disease
The symptoms of liver disease can vary depending on the underlying cause. However, some common symptoms of liver disease include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Jaundice
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dark urine
- Pale stool
Diagnosing Liver Disease
Liver disease can be diagnosed through various methods, including:
- Blood tests to evaluate liver function
- Imaging tests such as ultrasound and MRI
- Liver biopsy
Treating Liver Disease
The treatment for liver disease depends on the underlying cause. Some common treatments include:
- Lifestyle changes such as reducing alcohol consumption and maintaining a healthy weight
- Medications to manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease
- Liver transplant in severe cases
Prevention Of Liver Disease
Liver disease can be prevented by:
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Getting vaccinated for hepatitis A and B
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals
Liver disease is a severe condition that can impact the liver’s ability to function correctly. However, by understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments, it’s possible to manage liver disease effectively. If you’re experiencing any symptoms related to liver disease, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Liver King
Liver King is a renowned advocate for consuming nutrient-dense organ meats like liver. It is a powerhouse of essential vitamins, minerals, and nutrients, such as vitamin A, B12, and iron, crucial for optimal health and wellbeing. Incorporating liver into your diet can provide numerous health benefits and support overall wellness.
The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. One fascinating aspect of the liver is its nickname – the “. ” Let’s delve deeper into what makes the liver so remarkable and why it deserves this royal title.
The Powerhouse Of The Body
- The liver is the largest internal organ in the human body and carries out over 500 essential functions.
- It acts as a filtration system, removing toxins and waste products from our blood.
- The liver also produces bile, a substance that aids in the digestion and absorption of fats.
- Additionally, it stores essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron and vitamin A, for future use.
- The liver plays a critical role in regulating blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels, and hormone balance.
- It is responsible for metabolizing drugs and medications, making them effective and safe for our bodies.
Unparalleled Detoxification Abilities
- The liver is a master detoxifier, breaking down harmful substances like alcohol, drugs, and environmental toxins.
- It converts ammonia, a waste product of protein metabolism, into urea, which can be safely eliminated through urine.
- Through a process called biotransformation, the liver transforms fat-soluble toxins into water-soluble substances that can be excreted.
Regeneration And Resilience
- The liver has an extraordinary ability to regenerate itself. Even if a portion of the liver is surgically removed, it can regenerate and regain its full functionality within a matter of months.
- This remarkable regenerative capacity makes liver transplantation feasible and life-saving for individuals with severe liver diseases.
Maintaining Liver Health
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial for maintaining optimal liver function.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to provide essential nutrients for liver health.
- Limit the consumption of alcohol, as excessive alcohol intake can lead to liver damage and even liver cirrhosis.
- Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water daily to support liver function.
- Engage in regular exercise to promote blood circulation and overall liver health.
- Avoid the use of recreational drugs and be cautious with medications, following proper dosage instructions.
Remember, the liver is the true “king” when it comes to keeping our bodies functioning smoothly. By understanding its importance and taking care of it, we can ensure a healthy and well-functioning liver for a lifetime.
Liver Cancer
Liver cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cells of the liver. It can be a primary liver cancer, which starts in the liver, or a secondary liver cancer, which spreads from other parts of the body.
Symptoms may include jaundice, abdominal pain, and unexplained weight loss. Early detection and treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
Recognizing Liver Disease Symptoms
Liver disease symptoms can vary widely, ranging from mild to severe. Early detection is crucial for effective management. Here are some common signs and symptoms to watch out for:
- Abdominal pain: Discomfort or tenderness in the upper right area of the abdomen can indicate liver problems.
- Jaundice: The yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes is a classic symptom of liver disease, caused by the buildup of bilirubin.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy can be a result of liver dysfunction.
- Nausea and vomiting: Feeling sick to the stomach and experiencing vomiting may be associated with liver issues.
- Loss of appetite: A reduced desire to eat and unintended weight loss can be indicative of liver disease.
- Swelling: Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen and lower extremities, known as edema, can be a sign of liver damage.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can be linked to various conditions. so it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis if any of these signs are present.
Liver Disease Symptoms
Liver disease symptoms can include fatigue, jaundice, abdominal pain, and swelling. Other signs may include dark urine, pale stools, and loss of appetite. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment.
Where Is Your Liver?
The liver, one of the most vital organs in the human body, is located in the upper right side of the abdomen, beneath the diaphragm and above the stomach. It is the largest internal organ and plays a crucial role in various bodily functions.
Understanding the exact location of your liver is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Location And Position
- The liver is situated in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen.
- It is positioned just below the right lung and above the stomach.
- Additionally, it is nestled beneath the diaphragm, a large muscle that aids in breathing.
- The liver’s location allows it to perform its functions efficiently, such as detoxification and metabolizing nutrients.
Protection And Importance
- The liver is safeguarded by the rib cage & providing essential protection from external impact.
- Moreover, its strategic position ensures it can carry out its diverse functions effectively, contributing to overall health and wellness.
Understanding the location and positioning of the liver is crucial for comprehending its importance and the impact it has on overall health.
Where Is Your Liver?
Your liver is a vital organ located in the upper right side of your abdomen. It plays a crucial role in filtering toxins from your blood, producing bile for digestion, and storing nutrients.
The liver is a vital organ located in the human body. It plays a crucial role in various bodily functions and is positioned in the upper right side of the abdomen, just below the diaphragm. Let’s explore further to understand where exactly the liver is located and its significance.
Location Of The Liver:
- The liver is the largest internal organ in the human body and is situated on the right side of the abdomen.
- It is positioned under the rib cage, extending from the lower part of the right lung to the mid-abdomen.
- The liver is primarily located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, beneath the right dome of the diaphragm.
- It is nestled just below the right lung and next to the stomach, gallbladder, and intestines.
Anatomical Description Of The Liver:
- The liver is a reddish-brown organ with a smooth and soft texture.
- It has two main lobes, the right lobe, and the left lobe, which are separated by a band of connective tissue called the falciform ligament.
- The right lobe is larger and bulkier than the left lobe.
- The liver receives blood from two major sources: The hepatic artery, which supplies oxygenated blood, and the portal vein, which carries nutrient-rich blood from the digestive system.
- It consists of millions of tiny functional units called hepatocytes, which are responsible for various metabolic activities.
Importance Of The Liver:
- The liver performs over 500 vital functions in the body, making it an indispensable organ.
- It aids in digestion by producing bile, which helps break down fats in the small intestine.
- The liver filters and detoxifies harmful substances, such as drugs, alcohol, and toxins, from the blood.
- It stores vitamins, minerals, and glucose to provide essential nutrients to the body when needed.
- The liver plays a crucial role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
- It produces blood-clotting proteins and regulates blood sugar levels.
- Additionally, the liver is responsible for the synthesis and breakdown of cholesterol.
Understanding the location of the liver is essential in comprehending its functions and the impact it has on our overall health. Its strategic position in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen allows it to efficiently perform its various roles.
Now that we have explored the location and significance of the liver, let’s delve further into its remarkable functions in upcoming sections.
What Does The Liver Do?
The liver is a vital organ that performs many essential functions in the body. It plays a crucial role in detoxifying harmful substances, producing bile to aid in digestion, storing nutrients, and regulating blood sugar levels. Without a healthy liver, the body can suffer from a range of serious health problems.
The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. It is the largest glandular organ in the human body, located in the upper right portion of the abdomen, just beneath the diaphragm.
In this blog post, we will explore the liver’s location, its functions, and the importance of taking care of this incredible organ.
Where Is The Liver?
The liver is located in the upper right portion of the abdomen, just beneath the diaphragm. It is protected by the rib cage, which makes it difficult to feel or touch. Here are some key points about the liver’s location:
- The liver is the largest glandular organ in the human body.
- It is positioned in the upper right portion of the abdomen, just beneath the diaphragm.
- The liver is protected by the rib cage, which makes it difficult to feel or touch.
The liver is a crucial organ responsible for a variety of functions that are essential to our body’s overall health and well-being. Understanding the liver’s location is the first step in appreciating its importance and taking care of it.
Functions Of The Liver
The liver performs over 500 functions, making it one of the most essential organs in the body. Here are some key functions of the liver:
- Detoxification: The liver is responsible for filtering toxins from the blood, removing harmful substances that can damage our body.
- Metabolism: The liver processes nutrients from the food we eat, converting them into energy and storing them for later use.
- Production: The liver produces bile, a digestive juice that helps break down fats in the small intestine.
- Storage: The liver stores vitamins, minerals, and sugars, releasing them when needed.
- Immunity: The liver plays a crucial role in the immune system, producing proteins that fight off infections and diseases.
The liver’s functions are incredibly diverse, and it is crucial to keep this organ healthy to ensure that it can perform these functions effectively.
Importance Of Taking Care Of The Liver
The liver is a vital organ that performs several critical functions in our body. Taking care of the liver is essential to maintaining our overall health and well-being. Here are some tips for taking care of the liver:
- Eat a healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help keep the liver healthy.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help keep the liver healthy by reducing the risk of fatty liver disease.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Drinking alcohol in moderation is essential for liver health.
- Avoid exposure to toxins: Toxins can damage the liver, so it is essential to avoid exposure to harmful chemicals and pollutants.
- Get vaccinated: Certain viruses, such as hepatitis A and B, can damage the liver. Getting vaccinated can help protect against these viruses.
The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. Understanding its location, functions, and the importance of taking care of it is crucial to keep this organ healthy and functioning properly.
Where Is The Liver Located?
The liver is located in the upper right side of the abdomen, beneath the diaphragm. It plays a vital role in detoxification, digestion, and metabolism in the human body.
What Side Is Your Liver On?
Did you know that your liver is the largest solid organ in your body? It plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including metabolism, detoxification, and nutrient storage. But have you ever wondered what side your liver is on?
Let’s explore!
Location Of The Liver:
- The liver is located in the upper right side of your abdomen, just below your diaphragm.
- It extends slightly towards the left side of your body, crossing the midline.
- The liver is protected by your rib cage, making it difficult to feel or palpate.
Right Side Dominance:
- The right lobe of the liver is larger than the left lobe, occupying most of the abdominal space.
- It is positioned closer to the front of your body, making it more accessible during medical procedures.
- The right side dominance of the liver is due to the anatomical positioning and the need to accommodate other organs.
Left Side Functions:
- While the left lobe is smaller, it still performs important functions.
- The left lobe of the liver is responsible for filtering and processing blood, producing bile, and storing glycogen.
- It also plays a role in detoxification and metabolizing certain medications.
Lobes And Segments:
- The liver is divided into two main lobes: The right lobe and the left lobe.
- Each lobe is further divided into segments, with the right lobe having eight segments and the left lobe having four segments.
- This division helps in surgical procedures and enables targeted treatment of liver diseases.
Now that you know what side your liver is on, you can appreciate the importance of this vital organ. Its location on the upper right side of your abdomen, with a slight extension towards the left, allows it to perform its functions efficiently.
Understanding the anatomy of your liver can help you take better care of your overall health and well-being.
Where Is The Liver?
The liver is located on the right side of the abdomen, beneath the diaphragm. It plays a crucial role in filtering blood and producing bile to aid in digestion. This vital organ also stores energy and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Understanding The Location Of Your Liver
The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. Understanding the location of your liver is essential for grasping its significance in maintaining overall health and well-being. Let’s delve into where your liver is located and its anatomical positioning.
Location Of The Liver:
- The liver is situated in the upper right portion of the abdominal cavity, beneath the diaphragm.
- It is primarily positioned behind the lower ribs on the right side of the body.
- The liver spans across the midline of the body, extending slightly into the left side as well.
- Positioned just below the liver is the gallbladder, which is involved in the storage and concentration of bile produced by the liver.
Importance Of The Liver’s Location:
- The strategic placement of the liver allows it to efficiently process and filter blood from the digestive tract before distributing it to the rest of the body.
- Its proximity to the diaphragm facilitates the exchange of gases during the breathing process, aiding in the maintenance of respiratory functions.
- The liver’s location also enables it to regulate various metabolic processes, including the storage and release of glucose to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Understanding the location of your liver provides valuable insight into its pivotal role in sustaining overall health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Four Warning Signs Of A Damaged Liver?
The four warning signs of a damaged liver are: 1. Jaundice – yellowing of the skin and eyes. 2. Abdominal pain and swelling. 3. Dark urine and pale stools. 4. Fatigue and weakness. If you notice these symptoms, seek medical attention promptly.
Where Do You Feel Liver Pain?
Liver pain is usually felt in the upper right area of the abdomen. It can also radiate to the back or shoulder. If you’re experiencing any pain or discomfort, it’s important to seek medical attention.
What Foods Are Good For Liver Repair?
Foods that are good for liver repair include leafy greens, fatty fish, nuts, and olive oil. These foods are rich in antioxidants and healthy fats that help reduce inflammation and support liver health.
How Do I Make My Liver Healthy Again?
To make your liver healthy again, follow these steps: 1. Maintain a healthy weight 2. Limit alcohol intake 3. Avoid high-fat foods 4. Eat a balanced diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables 5. Exercise regularly.
Conclusion
The liver plays a vital role in keeping our body healthy and functioning properly. It is responsible for filtering toxins and waste products from our blood, producing bile to aid in digestion, and regulating our metabolism. Taking care of our liver is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing liver diseases.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle, such as exercising regularly, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and eating a balanced diet, we can support our liver’s health and ensure optimal functioning. Let’s prioritize our liver’s health and well-being to live a happy and healthy life.



