Vaginal depth is a topic that often surfaces in discussions about female reproductive anatomy, yet a myriad of myths and misconceptions surrounds it. Understanding vaginal depth involves exploring not only the basic anatomy of the vaginal canal but also recognizing how it varies among individuals and changes in different physiological states, such as sexual arousal or following childbirth.
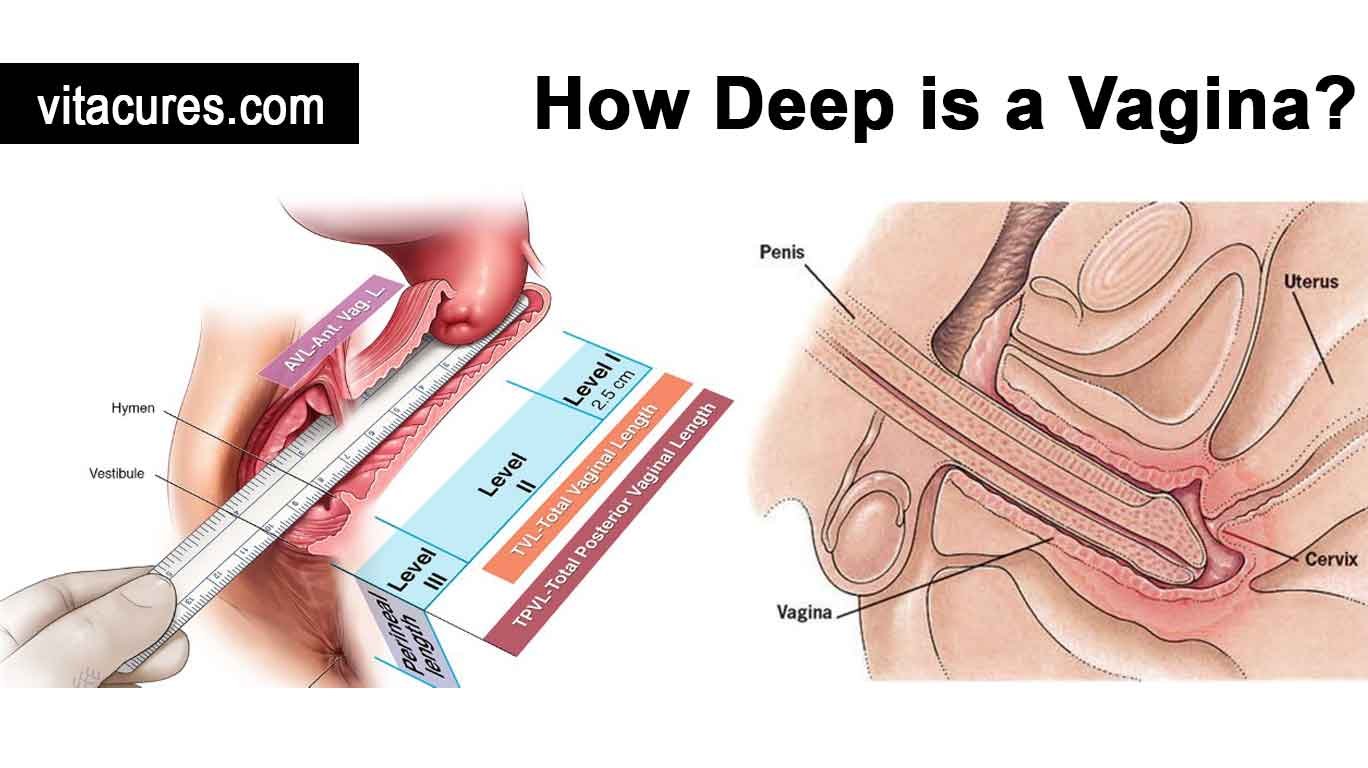
The vagina is a muscular, elastic tube that extends from the external female genitalia to the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus. Typically, the vaginal canal is about 7.5 to 10 centimeters (3 to 4 inches) in length when unaroused, but it can expand significantly during sexual arousal or childbirth due to its elastic nature. This flexibility is an evolutionary design intended to accommodate sexual intercourse and the birthing process.
In this exploration of vaginal depth, we will dispel common myths and provide insights into how vaginal depth can influence, or be influenced by, various health conditions, surgical procedures, and life stages. By understanding these aspects, individuals can gain a more comprehensive view of vaginal health and its implications on overall well-being.
How Deep is a Vagina?
Definition and Anatomy
The vagina is a flexible, muscular tube that connects the external genitals to the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus. The inner walls are pleated with ridges called rugae, which allow the vagina to expand during sexual intercourse and childbirth.
Structure of the Vaginal Canal
The vaginal canal is designed to be highly elastic, accommodating changes such as sexual arousal or childbirth. It’s surrounded by muscles that can tighten or relax, which helps during both sex and the delivery of a baby.
Length of the Vagina at Rest
Typically, the vagina measures between 7.5 to 10 centimeters (about 3 to 4 inches) when not aroused. This measurement can vary slightly from person to person.
Changes in Depth During Arousal
When a woman becomes sexually aroused, her vagina lengthens and widens in a process known as vaginal tenting. This change helps in making sexual activity more comfortable and enjoyable, allowing for deeper penetration without discomfort.
Average Measurements
Resting Depth of a Vagina
The average depth of a vagina in a resting, non-aroused state is usually around 3 to 4 inches. It’s important to note that like height or shoe size, vaginal depth varies from one woman to another.
Variation Among Individuals
Just as people differ in height and body shape, the depth of the vagina varies widely among women. Factors like genetics play a significant role in this variation.
Impact of Factors Like Age and Childbirth
As a woman ages or goes through childbirth, the elasticity and muscle tone of her vagina can change. Childbirth, especially multiple deliveries, can stretch the muscles and tissues of the vagina, sometimes leading to a slight increase in resting depth. However, exercises like Kegels can help strengthen pelvic floor muscles and improve muscle tone, which can influence the vaginal depth over time.
Factors Affecting Vaginal Depth
Physical Factors
- Biological Variation and Genetics
- Every woman’s body is unique, and just like other physical traits, the depth of the vagina is largely determined by genetics. This means that some women naturally have deeper vaginas due to their genetic makeup.
- Hormonal Changes
- Hormonal fluctuations throughout a woman’s life, such as those during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can affect the elasticity and the muscle tone of the vagina, potentially altering its depth.
- Effects of Pregnancy and Childbirth
- Pregnancy and childbirth are significant events that can change a woman’s vaginal depth. The muscles and tissues may stretch or tear during childbirth, which can increase the size of the vaginal canal. Although this can revert somewhat after delivery, repeated childbirths might lead to more lasting changes.
Sexual Arousal
- Vaginal Tenting (Expansion) During Arousal
- During sexual arousal, the vagina lengthens and widens, a process known as tenting. This is a natural response that prepares the vagina for penetration, making sex more comfortable and pleasurable.
- Role in Accommodating Penetration
- The increased depth and width during arousal are crucial for accommodating a partner during penetration. This flexibility helps prevent pain and discomfort during intercourse.
Medical Conditions
- Conditions like Vaginal Agenesis or Pelvic Floor Disorders
- Certain medical conditions can affect vaginal depth. Vaginal agenesis, a rare condition where the vaginal canal is underdeveloped or absent, directly impacts vaginal depth. Pelvic floor disorders, which involve a weakening of the muscles supporting the pelvic organs, can also alter the structural integrity of the vaginal canal.
- Surgeries That Can Impact Depth
- Various surgical procedures may alter the depth of the vagina. For example, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) can sometimes lead to a shortening of the vaginal canal. Other reconstructive surgeries may either increase or decrease vaginal depth depending on the nature and purpose of the procedure.
Understanding these factors provides insight into the natural variability of vaginal depth and highlights the complex interplay of genetics, physical condition, and medical history in determining this aspect of female anatomy.
Cultural and Social Perspectives on Vaginal Depth
Misconceptions About Vaginal Depth
Vaginal depth is a subject often clouded by myths and misunderstandings, which can influence cultural perceptions and individual self-esteem. Here’s a closer look at some prevalent misconceptions:
- Myths Related to Sexual Activity and Depth
- A common myth is that frequent sexual activity can permanently increase the depth and width of the vagina. This is not true; the vagina is highly elastic and returns to its normal size after intercourse. Changes in the vagina are temporary and primarily influenced by arousal, not the frequency of sexual activity.
- Common Societal Misunderstandings
- Society often incorrectly correlates vaginal depth with morality or sexual promiscuity. Such misconceptions can lead to negative body image and sexual insecurities among women. It’s crucial to challenge these baseless associations and promote understanding that like any other body part, the size and shape of the vagina vary widely and naturally.
Sexual Function and Pleasure
The role of vaginal depth in sexual pleasure is another area surrounded by myths and misinformation. Let’s explore the realities:
- Depth and Its Relationship to Pleasure
- While the depth of the vagina can slightly affect sexual pleasure, it is not a predominant factor. Sexual pleasure is influenced more by the sensitivity of the vaginal walls and clitoris. The G-spot, often cited in discussions of sexual satisfaction, is located only a few inches inside the vagina and is accessible regardless of vaginal depth.
- Communication Between Partners
- Effective communication is key to mutually satisfying sexual experiences. Partners should feel comfortable discussing their needs and preferences, including any concerns about physical compatibility. Such open discussions can dispel misconceptions and ensure that both partners are informed and attentive to each other’s comfort and pleasure.
Addressing Cultural Norms and Education
To combat the cultural stigmas and misunderstandings about vaginal depth, comprehensive sexual education and public health campaigns are essential. These should aim to:
- Educate about anatomical diversity: Teaching that variations in body anatomy, including vaginal depth, are normal and healthy can help reduce stigma and promote body positivity.
- Promote sexual health literacy: Providing accurate information about sexual anatomy and function can dispel myths and empower individuals, particularly women, in their sexual health.
- Encourage respectful communication: Cultivating a culture where discussing body differences and sexual preferences openly and respectfully can enhance intimacy and reduce misunderstandings in relationships.
Understanding the real factors that influence vaginal depth and its role in sexual pleasure is crucial for dismantling harmful myths and fostering a healthier, more informed society. By promoting accurate information and open communication, we can contribute to better sexual wellbeing and greater respect for body diversity.
Deep Vagina vs. Tight Vagina: A Misconception
The concepts of a “deep vagina” versus a “tight vagina” often permeate discussions about sexual anatomy, but these terms are steeped in misconceptions and misunderstandings about vaginal physiology. It’s crucial to clear up these myths and present factual information about vaginal elasticity and adaptability.
Understanding Vaginal Elasticity
Vaginal Elasticity Explained: The vagina is made up of flexible, muscular tissues that are highly elastic. This elasticity allows it to expand and contract as needed—for instance, during sexual intercourse or childbirth. The walls of the vagina are surrounded by a network of muscles that can relax to increase space or tighten to decrease it, all while returning to a normal resting state after the need for expansion passes.
Role of Elasticity in Sexual Function: Vaginal elasticity plays a crucial role in sexual function, ensuring comfort and accommodating variations in penis size, fingers, or sex toys during intercourse. This adaptability is vital for both sexual pleasure and reproductive functions.
Adaptability and Flexibility of Vaginal Walls
How the Vagina Adjusts:
- During Arousal: When aroused, the vagina undergoes “vaginal tenting,” which elongates and widens it. This change helps accommodate penetration and enhances sexual pleasure.
- During Childbirth: The vaginal canal can expand significantly to allow the passage of a baby, demonstrating its remarkable flexibility.
Post-Activity Reversion: After sex or childbirth, the vaginal muscles contract to return the canal to its usual size. This reversibility is a natural characteristic of the vaginal anatomy, contradicting the myth that frequent sexual activity or childbirth permanently stretches or loosens the vagina.
Separating Fact from Fiction
Common Myths:
- Myth: A “tight” vagina indicates limited sexual activity. Fact: Vaginal tightness is not related to sexual history; it is influenced by the natural muscle tone, which varies among individuals.
- Myth: Sexual satisfaction is dependent on vaginal depth or tightness. Fact: Sexual satisfaction is influenced more by factors such as emotional connection, communication, and clitoral stimulation rather than just penetration depth or tightness.
Educational Focus: Educating people about these realities is essential for dispelling myths and reducing the stigma associated with natural body variations. Awareness programs should focus on:
- The normal physiological range of vaginal elasticity and depth.
- The importance of understanding and respecting body diversity in enhancing sexual and reproductive health.
The distinction between a “deep” and a “tight” vagina is largely a fabrication of misconceptions. Real understanding comes from recognizing the natural elasticity and flexibility of the vagina, appreciating its ability to function and revert post-activity, and fostering open, informed discussions about sexual health. This knowledge empowers individuals to have healthier, more fulfilling sexual relationships free from misconceptions and stigma.
Medical and Scientific Insights on Vaginal Depth
Research Studies
Studies on Vaginal Depth and Variations: Research into vaginal depth and its variations has provided important insights into the natural diversity among women. Studies typically measure vaginal depth by inserting a speculum or similar device into the vagina while a woman is in a gynecological exam position. These studies reveal that vaginal depth can vary significantly between individuals, influenced by factors such as genetics, age, and hormonal levels.
How Depth Is Measured in Clinical Settings: In clinical settings, vaginal depth is most often measured as part of a pelvic exam. A gynecologist may use a marked speculum or a uterine sound (a long probe used to measure the depth of the uterus through the cervix) to obtain accurate measurements. This measurement helps in diagnosing conditions that may affect vaginal health or in planning surgical procedures.
Medical Procedures
Impact of Surgeries Like Hysterectomy on Depth:
- A hysterectomy, which involves the removal of the uterus, can impact the vaginal depth and structure, although the degree of impact can vary. Post-hysterectomy, the upper portion of the vagina may be sutured to create a new vaginal apex, which can slightly shorten the vaginal canal. However, most women do not notice a significant change in the functional depth of the vagina for sexual activity.
- Postoperative care and possible surgical adjustments are essential considerations to maintain vaginal depth and function after a hysterectomy.
Vaginal Reconstruction Options: Vaginal reconstruction is a branch of surgery that addresses various medical needs, including congenital abnormalities, trauma, cancer treatments, or gender affirmation surgeries. Here are a few common procedures:
- Vaginoplasty: This procedure creates or reconstructs the vagina using tissue from other parts of the body, such as the intestines or skin grafts. It is often used for women born without a vaginal canal (vaginal agenesis) or for transgender women during gender-affirming surgery.
- Laser Vaginal Rejuvenation: Aimed at enhancing vaginal tightness, this less invasive procedure uses laser technology to stimulate collagen production in vaginal tissues, which can improve elasticity and possibly affect perceived depth.
- Pelvic Floor Reconstruction: For women experiencing pelvic floor disorders (like prolapse), this surgery can reconstruct the pelvic floor muscles and ligaments, which can indirectly affect vaginal depth and function.
Medical and scientific research continues to evolve our understanding of vaginal depth, helping to refine treatments and surgeries that address the diverse needs of women. Knowing how vaginal depth varies and how it can be medically assessed and modified allows for better patient education and more personalized healthcare approaches.
Frequently Asked Questions about Vaginal Depth
Can Vaginal Depth Change Permanently?
Answer: Generally, the depth of the vagina does not change permanently under normal circumstances. It is designed to return to its typical depth after stretching during sexual intercourse or childbirth. However, certain medical conditions or surgeries, such as a hysterectomy or vaginal reconstruction, can alter the vaginal depth permanently. In cases of pelvic organ prolapse, where pelvic floor muscles weaken significantly, the functional depth of the vagina might also appear to change. But in many cases, treatments and exercises can help restore or maintain vaginal function and depth.
Is Vaginal Depth Related to Sexual Satisfaction?
Answer: Vaginal depth is not a major determinant of sexual satisfaction for most people. Sexual satisfaction is influenced more by factors such as emotional intimacy, physical compatibility, effective communication, and clitoral stimulation rather than the depth of penetration. Misconceptions persist about the role of vaginal depth in sexual pleasure, but it is important to understand that pleasure is a complex interplay of many physiological and psychological factors.
What Are the Common Methods to Measure Vaginal Depth?
Answer:
- During a Gynecological Exam: The most common clinical method for measuring vaginal depth involves using a speculum or a similar device during a pelvic exam. A gynecologist may insert a speculum, which is gently opened to allow for visual inspection and measurement of the vaginal walls and cervix.
- Using a Uterine Sound: Another method involves using a uterine sound, a long, thin probe that can be gently inserted through the cervix to measure the length from the entrance of the vagina to the cervix. This method is often used to prepare for procedures like IUD insertions.
- Imaging Techniques: In certain medical settings, ultrasound or MRI might be used to get detailed images of the vaginal canal and surrounding structures. These imaging techniques can be helpful in planning surgical treatments or diagnosing conditions.
Each of these methods should be performed by a healthcare professional in an appropriate setting to ensure safety and accuracy. These measurements are important for both diagnostic and treatment purposes, helping to tailor medical care to individual anatomical needs.
Complementary Topics on Vaginal Health
Vaginal Anatomy Overview
The vagina is a key component of the female reproductive system, extending from the vulva to the cervix, the lower part of the uterus. It serves several functions including the passage for menstrual flow, receiving sperm during intercourse, and serving as the birth canal. The walls of the vagina are lined with a mucous membrane and contain layers of muscle that are highly elastic, allowing for significant stretching during intercourse and childbirth.
Role of the Pelvic Floor Muscles
Function and Importance: The pelvic floor muscles provide support for the pelvic organs, including the bladder, intestines, uterus, and vagina. These muscles are crucial for maintaining continence and are actively involved during sexual activity by helping to control the tension and relaxation of the vaginal muscles.
Strengthening Exercises: Pelvic floor exercises, commonly known as Kegel exercises, can strengthen these muscles, improving both urinary and fecal incontinence, and enhancing sexual pleasure. Consistent practice of these exercises can help in maintaining pelvic health, particularly after childbirth or during menopause.
Common Issues Affecting the Vaginal Canal
Vaginal Prolapse: Vaginal prolapse occurs when the pelvic floor muscles and ligaments stretch and weaken, providing inadequate support for the vagina. This can lead to one or more sections of the vagina protruding through the vaginal opening. Symptoms may include discomfort, a feeling of heaviness in the pelvis, and urinary incontinence. Treatment options range from physical therapy to improve muscle strength to surgical intervention in more severe cases.
Vaginal Atrophy: Associated primarily with menopause, vaginal atrophy involves thinning, drying, and inflammation of the vaginal walls due to a decrease in estrogen levels. Symptoms include vaginal dryness, itching, pain during intercourse, and increased urinary frequency or urgency. Treatment typically involves hormonal therapies, such as topical estrogen creams, which can help replenish the levels and alleviate symptoms.
Infections and Inflammations: Common conditions such as yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can affect the vaginal canal, leading to symptoms like abnormal discharge, odor, itching, and pain. Maintaining good vaginal hygiene and seeking timely medical consultation can prevent and manage these issues effectively.
Understanding the anatomy and function of the vagina and pelvic floor muscles is essential for maintaining female pelvic health. Awareness of common vaginal issues allows for early identification and appropriate treatment, which can significantly improve a woman’s quality of life and sexual health. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, appropriate screenings for infections, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are key preventive measures.
Search Intent Classification for Vaginal Depth Content
Understanding the various types of search intent can guide content creators and medical professionals in delivering information that aligns with the needs and motivations of different users. Here’s how content about vaginal depth and related topics can be classified based on search intent:
Informational Intent
Users with informational intent are looking for knowledge or data. They want to understand a topic in detail. In the context of vaginal depth, informational content might include:
- Understanding Vaginal Depth and Its Variations: Articles or blog posts explaining how vaginal depth can differ from one person to another and the factors that influence these variations.
- Scientific Explanations and Anatomy: Detailed content that explains the anatomical structure of the vagina, how and why it changes under certain conditions (like arousal or after childbirth), and the scientific principles underlying these changes.
Navigational Intent
Navigational intent is about users trying to find a specific website or page. For vaginal health, navigational queries might direct users to:
- Finding Credible Resources on Vaginal Health: Directing to trustworthy medical websites, online medical journals, or patient education portals that offer scientifically accurate information about vaginal health.
- Accessing Medical or Sexual Health Advice: Links to specific health service providers, such as sexual health clinics, or platforms where users can get personalized advice from healthcare professionals.
Transactional Intent
Users with transactional intent are ready to perform an action, such as making a purchase or booking an appointment. Relevant transactional content for vaginal health could include:
- Seeking Consultations with Gynecologists: Facilitating online bookings for appointments with gynecologists or specialists in women’s health. This could be through medical practice websites or health service apps.
- Purchasing Products Related to Vaginal Health: E-commerce pages where users can buy health-related products such as probiotics for vaginal health, pH-balanced washes, moisturizers, or hormonal creams recommended by healthcare providers.
By aligning content with the appropriate search intent, healthcare providers and content creators can effectively meet the informational, navigational, and transactional needs of their audience. This approach not only enhances user satisfaction but also increases the likelihood of the content achieving its intended purpose, whether that’s educating, directing, or facilitating a purchase or appointment.
Content Suggestions for Educating and Engaging Audiences on Vaginal Depth
To effectively disseminate information and engage users on the topic of vaginal depth and related subjects, a variety of content formats can be utilized. Each format can cater to different user preferences and learning styles, increasing the accessibility and comprehensibility of the information.
Articles
- “How Deep is the Average Vagina? Separating Fact from Fiction”
- This article can explore common myths and provide factual information based on scientific research about the average depth of the vagina. It could include expert opinions from gynecologists and references to medical studies to provide a well-rounded view.
- “Vaginal Anatomy: What You Need to Know”
- Aimed at readers looking for a deeper understanding of vaginal anatomy, this piece could detail the structures, functions, and roles of the vagina within the reproductive system. It can also discuss how these features relate to overall health and sexual function.
Videos
- Explainers on Vaginal Depth and Flexibility
- Short, engaging explainer videos that illustrate how vaginal depth varies among individuals and changes in different situations, such as arousal or childbirth. Using animations and visuals, these videos could help demystify the subject for a broad audience.
Infographics
- Visual Representation of Vaginal Anatomy and Depth
- Infographics are excellent for visually summarizing complex information. An infographic on this topic could include diagrams of the vaginal canal, show how depth can change, and incorporate quick facts to educate the public in an easily digestible format.
FAQs and Expert Answers
- Addressing Common Myths and Concerns
- A dedicated FAQ section where experts address common questions and concerns about vaginal depth could be very beneficial. This section can tackle myths directly, provide reassuring medical advice, and guide individuals on when to seek professional health advice.
Deployment Strategies
- Social Media Campaigns: Share infographics and short video clips on platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter to reach a wider audience.
- Educational Webinars and Live Q&A Sessions: Organize sessions where medical professionals answer live questions from the audience, providing a direct and interactive way to address personal concerns and debunk myths.
- Collaborations with Health Influencers: Partner with influencers in the health and wellness space to share content and extend its reach to a broader audience who trusts and follows their advice.
These content suggestions and strategies are designed to educate the public on vaginal health in a respectful, informative, and engaging manner. By providing reliable information in various formats, it becomes possible to improve knowledge and dispel myths related to vaginal anatomy and health.