Fluoride in water is a common topic of debate. Many people wonder if it is safe for their health.
Fluoride is often added to drinking water to help prevent tooth decay. It has benefits, but concerns also exist. Some studies suggest that too much fluoride can cause health issues. This makes it important to understand both sides of the argument.
Questions arise about its safety, especially for children and pregnant women. Knowing the facts can help you make informed choices about your drinking water. We will explore the benefits and risks of fluoride in water. We aim to provide clear information to help you decide what is best for your health and your family’s health.

The Fluoride Debate
The discussion about fluoride in water is ongoing. Many people have strong opinions. Some believe fluoride helps dental health. Others worry about its safety. This section explores the origins and current concerns about fluoride.
Origins Of Water Fluoridation
Water fluoridation began in the 1940s. Scientists found that fluoride reduces tooth decay. Communities started adding fluoride to public water systems. This practice aimed to improve dental health for everyone.
Key points about the origins of fluoridation:
- First city to fluoridate water: Grand Rapids, Michigan.
- Supported by the American Dental Association.
- Believed to lower cavities by 20-40%.
Contemporary Concerns
Today, concerns about fluoride have grown. Some studies suggest health risks. These include potential links to:
- Dental fluorosis: a condition causing white spots on teeth.
- Bone health issues: possible weak bones or fractures.
- Thyroid problems affect hormone production.
Public opinion is divided:
| Opinion | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Support Fluoridation | 70% |
| Oppose Fluoridation | 30% |
Many people want to know the truth. Is fluoride safe? Is it worth the benefits? This debate continues as more research emerges.
Fluoride 101
Fluoride is a common topic in health discussions. Many people wonder about its safety. Understanding fluoride is crucial. This section will cover the basics.
Defining Fluoride
Fluoride is a natural mineral. It occurs in soil, water, and some foods. It helps protect teeth from decay. Many dental products contain fluoride. These include toothpaste and mouth rinses. The aim is to reduce cavities.
Fluoride works by:
- Strengthening tooth enamel
- Reversing early signs of tooth decay
- Inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria
Natural Vs. Artificial Fluoride
Fluoride can be natural or artificial. Natural fluoride is found in water sources. It comes from rocks and minerals. Many areas have natural fluoride levels. These levels vary widely.
Artificial fluoride is added to water supplies. This process is known as fluoridation. The goal is to improve dental health for communities. Here is a comparison:
| Type of Fluoride | Source | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Fluoride | Found in nature (soil, water) | Dental health, food |
| Artificial Fluoride | Added to water | Preventing cavities |
Understanding these types helps clarify health discussions. Many support fluoride for its benefits. Others express concerns about safety. Knowing the facts is essential.
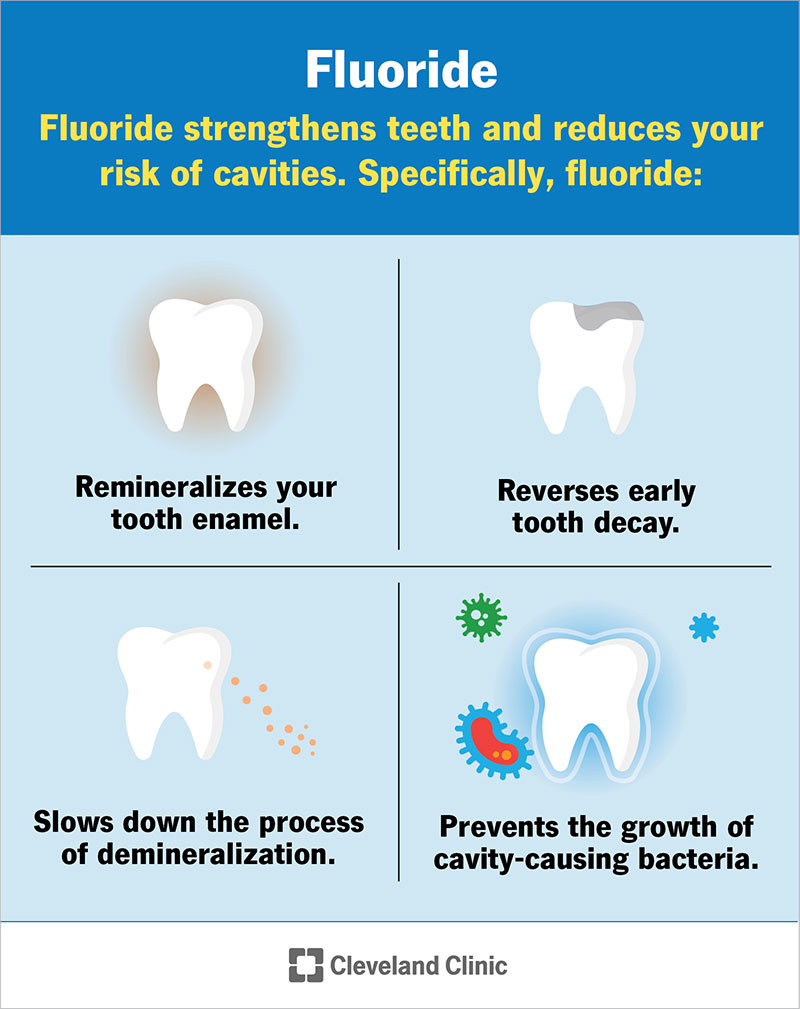
Health Benefits Of Fluoride
Fluoride is known for its positive effects on dental health. It helps to protect teeth and prevent cavities. Many communities add fluoride to their water supply. This practice aims to improve oral health for everyone. Let’s explore the specific health benefits of fluoride.
Preventing Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is a common problem for many people. Fluoride plays a crucial role in preventing this issue. It does this by:
- Reducing the ability of bacteria to produce acid.
- Helping to remineralize teeth after acid attacks.
- Strengthening the overall structure of teeth.
Research shows that communities with fluoridated water have lower rates of tooth decay. This is especially true for children. Studies indicate that fluoride can reduce cavities by up to 25% in children and adults.
Strengthening Enamel
Enamel is the protective outer layer of our teeth. Strong enamel helps prevent cavities and decay. Fluoride enhances enamel strength in two main ways:
- Fluoride bonds with the enamel, making it more resistant to acid.
- It helps create a stronger enamel layer during tooth development.
With stronger enamel, teeth can better withstand daily wear and tear. This means healthier teeth and fewer dental visits.
In summary, fluoride provides essential health benefits. It prevents tooth decay and strengthens enamel. These factors contribute to better oral health overall.
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Safety Standards
Understanding safety standards for fluoride in water is vital. These standards help protect public health. They ensure the levels of fluoride are safe for everyone.
Regulatory Guidelines
Different organizations set guidelines for fluoride levels in water. Here are some key points:
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Sets the maximum allowable level of fluoride in drinking water.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): recommends optimal fluoride levels for dental health.
- World Health Organization (WHO): Provides international safety standards for fluoride consumption.
The EPA limits fluoride to 4.0 mg/L in drinking water. The CDC suggests a level of 0.7 mg/L for dental benefits. These limits aim to protect both children and adults.
Monitoring Water Quality
Regular monitoring is essential for water safety. Local water utilities test fluoride levels. They must report these levels to the public.
Key methods of monitoring include:
- Collecting water samples.
- Testing for fluoride concentration.
- Checking for other contaminants.
Utilities must follow strict procedures. These ensure water remains safe to drink. Transparency is crucial. Residents should have access to water quality reports.
| Organization | Fluoride Level (mg/L) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| EPA | 4.0 | Maximum allowable level |
| CDC | 0.7 | Optimal level for dental health |
| WHO | 1.5 | International safety standard |
Understanding these standards helps you make informed decisions. It is important to stay updated on local water quality. Your health depends on safe drinking water.
Potential Risks
Fluoride in drinking water has benefits, but it also poses risks. Understanding these risks is important for your health. Some people may experience negative effects from fluoride exposure. Here, we explore the potential risks associated with fluoride in water.
Fluorosis Explained
Fluorosis is a condition caused by excessive fluoride intake. It mainly affects children under eight years old. Here are key points about fluorosis:
- Types of Fluorosis:
- Mild fluorosis: white spots on teeth.
- Moderate fluorosis: brown stains and pitting.
- Severe Fluorosis: severe damage to tooth enamel.
- Causes: High fluoride levels during tooth development.
- Prevention: Monitor fluoride sources, especially for children.
Other Health Impacts
Fluoride may affect health in ways beyond dental issues. Some studies suggest links to various health concerns:
| Health Concern | Description |
|---|---|
| Bone Health | Excessive fluoride may weaken bones over time. |
| Thyroid Issues | High fluoride levels can affect thyroid function. |
| Neurological Effects | Some studies link fluoride to lower IQ in children. |
Research continues on fluoride’s long-term health effects. Stay informed. Talk to your doctor about any concerns.
Scientific Evidence
Understanding fluoride safety requires looking at scientific evidence. Many studies examine its effects on health. Here, we explore the research and expert opinions on fluoride in water.
Research On Fluoride Safety
Numerous studies have explored the safety of fluoride in drinking water. Some key findings include:
- Dental Health: Fluoride helps prevent tooth decay. Many studies show lower cavity rates in communities with fluoridated water.
- Bone Health: Some research suggests fluoride may strengthen bones. However, excessive fluoride can lead to bone issues.
- Potential Risks: A few studies indicate high fluoride levels may link to health problems. These include thyroid issues and lower IQ in children.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) supports fluoride for dental health. The CDC states that water fluoridation is safe at recommended levels.
Expert Opinions
Experts have differing views on fluoride safety. Here are some notable opinions:
| Expert | Position |
|---|---|
| American Dental Association | Supports water fluoridation for its dental benefits. |
| World Health Organization | Recommends fluoride in small amounts for dental health. |
| Environmental Working Group | Raises concerns about high fluoride levels affecting health. |
Experts agree on the importance of balanced fluoride levels. Too little may harm dental health, while too much can cause problems.
Research continues to provide insights. As studies evolve, so does our understanding of fluoride’s safety.
Public Perception
Many people have strong feelings about fluoride in drinking water. Some believe it helps teeth, while others worry about health risks. Understanding public perception is key to this debate.
Media Influence
The media plays a big role in shaping opinions. News articles, social media posts, and documentaries can sway public thoughts.
Some media portray fluoride as a miracle for dental health. Others highlight potential dangers. This mixed messaging creates confusion.
Studies show that stories about fluoride can affect how people feel about it. Positive articles lead to more support. Negative stories raise concerns.
Here are some common media themes:
- Health benefits: Articles focus on how fluoride fights cavities.
- Risks: Reports highlight possible links to health problems.
- Government control: Some view fluoride as a way for the government to control health.
Public Surveys And Opinion
Surveys show varied opinions on fluoride. Some people trust it; others do not. Here is a summary of survey findings:
| Opinion | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Support Fluoride | 60% |
| Oppose Fluoride | 30% |
| Unsure | 10% |
Supporters often cite dental health benefits. They believe fluoride reduces cavities.
Opponents worry about safety. They often mention concerns about long-term exposure.
People who are unsure may need more information. They want to learn about both sides.
Overall, public perception is mixed. It reflects different beliefs and knowledge levels about fluoride.
Credit: www.nbcnews.com
Global Perspectives
Understanding fluoride in water requires a global look. Different countries have different views. Some countries embrace fluoridation. Others reject it. These choices shape public health.
Fluoridation Policies Worldwide
Fluoride use varies widely across the globe. Here is a summary of fluoridation policies:
| Country | Fluoridation Status | Population Affected |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Widespread | Approximately 74% of the population |
| Canada | Mixed | Approximately 40% of the population |
| European Union | Varies | Some countries fluoridate; others do not |
| Japan | Limited | Only a few areas |
| Brazil | Widespread | Majority of the population |
These differences reflect local health policies. They also show cultural attitudes towards fluoride.
Case Studies
Case studies provide insight into fluoride’s impact. Here are two notable examples:
-
Australia:
Fluoride was added to water in the 1950s. Rates of tooth decay dropped significantly. Communities reported better dental health.
-
Sweden:
Fluoride is not added to water. Instead, they focus on dental care education. The country sees low rates of tooth decay.
These cases show diverse outcomes. They highlight the importance of local health strategies. Understanding these can guide future policies.
Environmental Impact
The presence of fluoride in drinking water raises concerns about its impact on the environment. Understanding how fluoride interacts with nature is crucial. This section explores its effects on ecosystems and wildlife.
Fluoride In The Ecosystem
Fluoride enters the ecosystem through various sources:
- Water treatment plants
- Industrial discharge
- Runoff from agricultural areas
Once in the environment, fluoride can affect soil and water quality. It may accumulate in plants and animals. This accumulation can disrupt local ecosystems.
Effects On Wildlife
Fluoride can harm various wildlife species. The following effects have been observed:
| Wildlife Species | Potential Effects |
|---|---|
| Fish | Altered behavior and reproduction |
| Birds | Decreased population and reproductive issues |
| Amphibians | Developmental problems and increased mortality |
Studies show that high fluoride levels can lead to:
- Reduced fertility in fish.
- Impaired growth in amphibians.
- Increased vulnerability to diseases in birds.
These effects can lead to reduced biodiversity. Healthy ecosystems rely on all species. Protecting wildlife is vital for maintaining balance.

Credit: ilikemyteeth.org
Alternative Views
Many people have different opinions about fluoride in water. Some support it for dental health. Others raise concerns about safety. Let’s explore these alternative views.
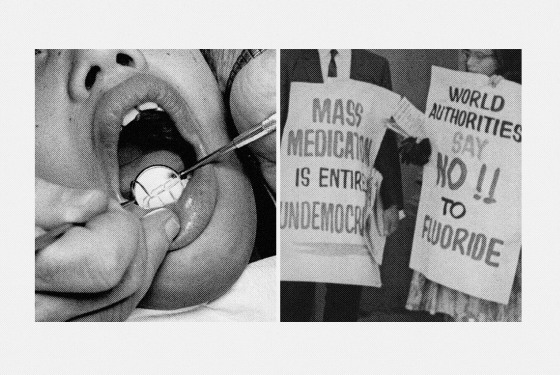
Anti-fluoridation Movements
Groups against fluoride argue it can harm health. They believe it may cause:
- Dental fluorosis, which affects teeth.
- Bone problems due to high fluoride levels.
- Potential links to neurological issues.
These movements often share their views through:
- Public campaigns.
- Social media posts.
- Community meetings.
Many anti-fluoridation advocates push for
- Testing water for fluoride levels.
- Removing fluoride from public water systems.
- Raising awareness about health risks.
Natural Water Advocacy
Natural water advocates promote unfluoridated sources. They believe in the benefits of:
- Pure spring water.
- Rainwater harvesting.
- Reverse osmosis systems.
Supporters of natural water argue that:
- Natural water is healthier.
- Fluoride is not needed for good dental health.
- People should have a choice in their water source.
They often focus on the importance of:
- Organic and sustainable practices.
- Reducing chemical exposure.
Legal And Ethical Considerations
The addition of fluoride to drinking water raises important legal and ethical questions. Many people feel that water fluoridation is a form of medication. Others argue it is a public health measure. This section explores these issues and their implications for health and rights.
Mandated Medication?
Fluoride in water can be seen as a mandated medication. It is added to prevent tooth decay. This raises some key questions:
- Is it ethical to medicate the public without consent?
- Can individuals refuse fluoride treatment?
- What are the health risks of fluoride?
Some argue that water should not be a delivery method for medication. Others believe it is a necessary health measure for everyone.
Rights And Regulations
Water fluoridation involves both rights and regulations. Different countries have different laws about fluoride. Here are some points to consider:
| Country | Fluoride Policy |
|---|---|
| United States | Fluoridation is common in many areas. |
| European Union | Some countries ban water fluoridation. |
| Australia | Fluoridation is widespread but not mandatory. |
Public health laws often support fluoride use. Yet, some people argue it violates their rights. The balance between public health and personal choice is complex.
Fluoride In Dental Products
Fluoride plays an important role in dental health. Many dental products contain fluoride. This helps prevent tooth decay. Understanding its use in toothpaste and mouthwashes is key.
Toothpaste And Mouthwashes
Toothpaste and mouthwashes often have fluoride. They help strengthen teeth. Here are some benefits:
- Reduces cavities
- Strengthens enamel
- Promotes overall oral health
Most dentists recommend fluoride toothpaste. It is effective in fighting decay. Mouthwashes with fluoride can offer extra protection. They reach areas that brushing may miss.
Comparing Efficacy
Different products have varied amounts of fluoride. Here is a comparison:
| Product Type | Fluoride Content (ppm) | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Toothpaste | 1000 – 1500 | Highly effective against cavities |
| Mouthwash | 225 – 900 | Good for additional protection |
Using both can enhance dental health. Toothpaste cleans, while mouthwash provides extra fluoride. Regular use is key for best results.
Consumer Choices
Many people care about what goes into their bodies. Fluoride in water is a big topic. Some like it for dental health. Others worry about safety. Understanding your options is important.
Fluoride-free Options
Many products do not contain fluoride. Here are some choices:
- Fluoride-Free Toothpaste: Many brands offer fluoride-free versions.
- Bottled Water: Check for fluoride levels on the label.
- Water Filters: Some filters remove fluoride.
People often choose these products for various reasons. Some want to avoid fluoride completely. Others may prefer natural options. It’s essential to research what works best for you.
Understanding Labels
Reading labels can be tricky. Here are some tips:
- Look for “fluoride-free”: Some products clearly state this.
- Check ingredients: Identify any fluoride compounds.
- Understand Water Sources: Know if the water is treated.
It helps to compare brands. Some may contain fluoride, while others do not. A simple table can help summarize this:
| Product Type | Fluoride Content |
|---|---|
| Fluoride-Free Toothpaste | No Fluoride |
| Bottled Water | Varies |
| Water Filters | Can Remove Fluoride |
Understanding these labels helps make informed choices. Your health matters. Choose what feels right for you.
Technological Advancements
New technologies help us understand fluoride’s impact on health. Innovations in water treatment and dental care improve safety. These advancements make it easier to manage fluoride levels. Let’s explore two key areas: water filtration systems and innovations in dentistry.
Water Filtration Systems
Water filtration systems play a vital role in managing fluoride levels. Different types of filters can reduce fluoride in drinking water. Here are some common filtration methods:
- Activated Alumina Filters: These filters effectively remove fluoride.
- Reverse osmosis systems filter out many contaminants, including fluoride.
- Distillation Units: Boiling water removes fluoride through evaporation.
Choosing the right filtration system is essential. Consider these factors:
| Filter Type | Effectiveness | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Activated Alumina | High | Moderate |
| Reverse Osmosis | Very High | High |
| Distillation | High | Moderate |
These systems help ensure safe drinking water. They can reduce fluoride levels significantly. Homeowners should evaluate their needs carefully.
Innovations In Dentistry
Dental care has seen many innovations over the years. New treatments focus on fluoride’s effects. Some key advancements include:
- Fluoride varnishes: These are applied directly to teeth. They help prevent decay.
- Silver Diamine Fluoride: This treatment can stop cavities.
- Personalized Fluoride Treatments: Dentists recommend tailored fluoride use.
These innovations increase dental health awareness. They also help manage fluoride exposure. Patients can discuss options with their dentists. Understanding individual needs is crucial for safety.
Moving Forward
Discussions about fluoride in water continue. Many people wonder about its safety and effectiveness. As we move forward, it’s important to explore new ideas and community involvement.
Future Of Fluoridation
The future of fluoridation looks at different factors. Here are some key points:
- Scientific studies will guide decisions.
- New technologies may improve fluoridation methods.
- Local governments will assess community needs.
Research focuses on the balance between benefits and risks. Some experts suggest adjusting fluoride levels based on local health data. Others call for more studies on long-term effects.
Community Engagement
Community involvement is crucial for informed choices. Here are ways to engage:
- Hold public meetings to discuss fluoride.
- Provide clear information on health impacts.
- Encourage feedback from residents.
Engagement builds trust. It helps families understand fluoride’s role in health. Transparency is key in all discussions.
Communities can create surveys. These can gauge opinions and concerns about water fluoridation. Understanding local views can shape future policies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is fluoride in drinking water harmful?
Fluoride in drinking water is generally considered safe at regulated levels. It helps prevent tooth decay and promotes oral health. However, excessive fluoride can lead to dental fluorosis or other health issues. It’s essential to monitor fluoride levels in your water supply for safety.
What Are The Benefits Of Fluoride In Water?
Fluoride in water strengthens tooth enamel and reduces cavities. It supports overall dental health, especially in children. Studies show that communities with fluoridated water have lower rates of tooth decay. This makes fluoride a valuable addition to public water systems.
How Does Fluoride Affect Children’s Health?
Fluoride supports healthy tooth development in children. It helps prevent cavities and strengthens enamel during crucial growth stages. However, excessive fluoride exposure may lead to dental fluorosis. Parents should ensure children consume fluoride in recommended amounts for optimal benefits.
Can Fluoride Cause Any Health Issues?
While fluoride is safe at regulated levels, excessive intake can lead to health concerns. Dental fluorosis is the most common issue, affecting tooth appearance. Some studies suggest possible links to other health problems, but more research is needed. Always check local water fluoride levels to stay informed.
Conclusion
Fluoride in water has both supporters and critics. Many studies show it helps prevent tooth decay. Yet, some people worry about possible health risks. Understanding these views is important. Always research and consider your local water quality. Talk to your doctor if you have concerns.
Your health is a priority. Make informed choices for you and your family. Stay aware of the latest information on fluoride. Knowledge helps you decide what’s best for your health.



